
In today’s globalized world, the movement of people across borders is a common occurrence. However, it’s crucial to recognize and understand the distinctions between different categories of individuals on the move, such as migrants, refugees, and asylum seekers. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they carry distinct legal and conceptual meanings. This article aims to clarify the differences among migrants, refugees, and asylum seekers, shedding light on their unique circumstances and the reasons behind their movements.
Migrants:
Migrants are individuals who choose to move from one place to another for various reasons, such as economic opportunities, family reunification, or personal preferences. Unlike refugees and asylum seekers, migrants are not forced to leave their home countries due to persecution, conflict, or human rights violations. Migration can be voluntary, and individuals often make these decisions in pursuit of a better quality of life, improved job prospects, or a desire for new experiences.
Key Points:
- Voluntary movement for various reasons.
- No requirement for international protection.
- Diverse motivations, including economic, educational, or personal factors.

Refugees:
Refugees are individuals who flee their home countries due to well-founded fears of persecution based on race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or political opinion. The 1951 Refugee Convention and its 1967 Protocol define the legal status and rights of refugees. International protection is granted to refugees to ensure their safety and well-being, and they are often unable or unwilling to return to their home countries due to the risks they face.
Key Points:
- Forced to flee due to persecution or violence.
- Specific legal criteria for refugee status.
- Entitled to international protection and assistance.

Asylum Seekers:
Asylum seekers are individuals who have left their home countries and are seeking international protection but have not yet been granted refugee status. They may have fled persecution or violence and are in the process of applying for asylum in another country. The determination of asylum status involves a thorough examination of the individual’s claims to ensure they meet the criteria outlined in international refugee law.
Key Points:
- Seeking international protection but not yet granted refugee status.
- Pending the outcome of the asylum application process.
- Entitled to certain rights and protections during the assessment period.
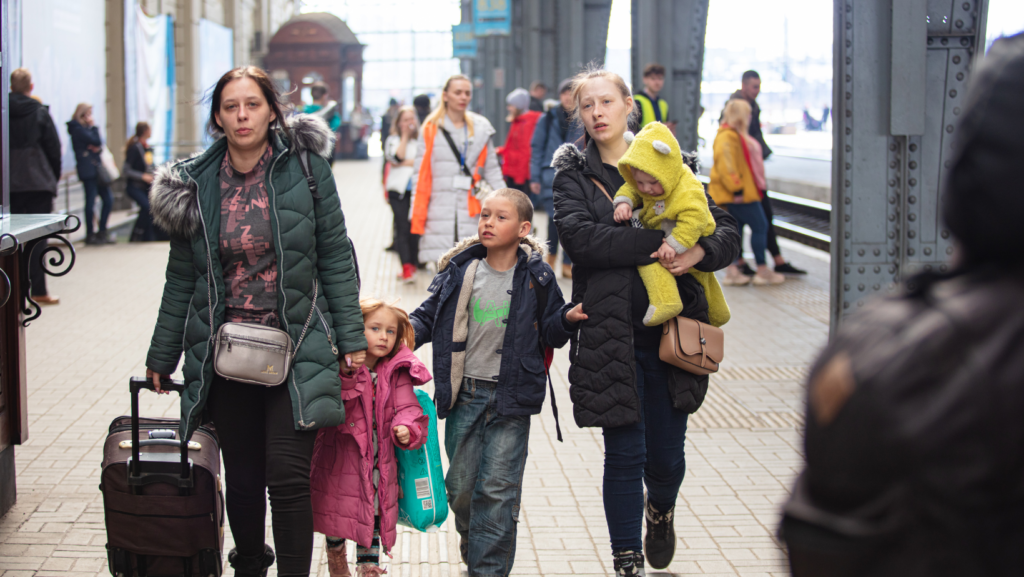
Understanding the differences between migrants, refugees, and asylum seekers is essential for promoting informed discussions and policies surrounding migration. While migrants move voluntarily for various reasons, refugees and asylum seekers are forced to leave their homes due to persecution or violence. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for ensuring that the rights and needs of vulnerable populations are adequately addressed on both national and international levels. By having a deeper understanding of these terms, societies can work towards more compassionate and effective responses to the complex challenges of forced displacement.
